Supermarket Loyalty Card Data Utilized to Identify Cancer Risks
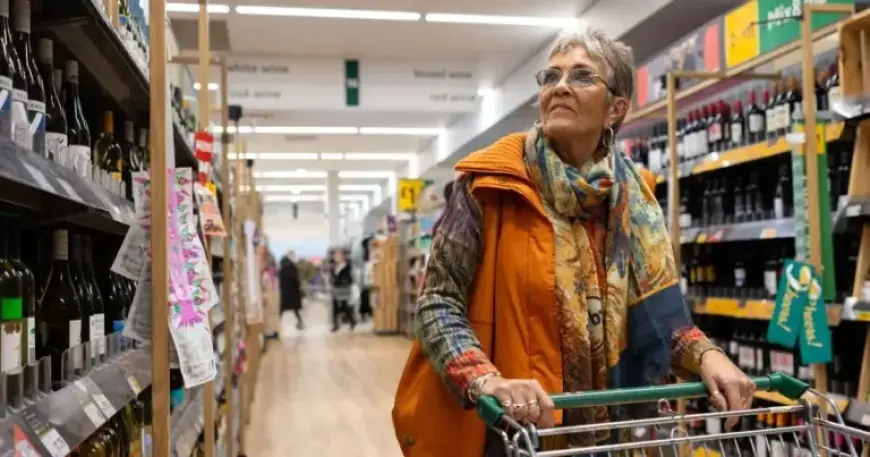

Recent research suggests that supermarket loyalty card data could play a crucial role in the early diagnosis of cancer. A significant study is set to recruit nearly 3,000 participants to explore the link between shopping habits and the early indicators of ten different cancer types.
Study Overview and Objectives
This groundbreaking research will analyze shopping patterns, particularly focusing on data from Tesco Clubcard and Boots Advantage Card users. The investigation aims to identify purchasing trends that may serve as early warning signs for various cancers, including:
- Bowel cancer
- Bladder cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Liver cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
Previous Insights on Cancer Indicators
The research team previously established that an increase in purchases of painkillers and indigestion medications could indicate early signs of ovarian cancer. Now, they aim to extend their findings to other cancer types by examining the shopping habits of 1,450 cancer patients alongside 1,450 healthy individuals.
Potential Impact on Cancer Detection
Professor James Flanagan, the study leader from Imperial College London, expressed optimism about the potential impact of this study. He stated that it could revolutionize how everyday data is utilized to enhance public health understanding.
Many cancers present mild or nonspecific symptoms such as bloating or fatigue, leading individuals to self-medicate. By tracking minor shifts in shopping behavior, researchers hope to develop a digital alert system that prompts shoppers to consult healthcare professionals.
Collaborative Efforts and Support
This important study is supported by major players in retail. Boots, with a large customer base using the Advantage Card, highlights the advantages of leveraging everyday shopping data to identify healthcare warning signs.
Marc Donovan, Boots’ healthcare development director, noted that over a quarter of the UK population holds a Boots Advantage Card. He emphasized the transformative power of responsibly used shopping data in enhancing cancer detection.
Oonagh Turnbull, from Tesco, also underscored the importance of customer involvement. She hopes that sharing Tesco Clubcard data will contribute to saving lives by facilitating early detection of certain cancers.
Conclusion
This innovative approach to cancer risk assessment through supermarket loyalty cards marks a significant step forward in healthcare. As researchers analyze shopping data, there is potential to reshape early diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving health outcomes for patients.