Unveiling the Intricate Architecture of the Egg Nebula
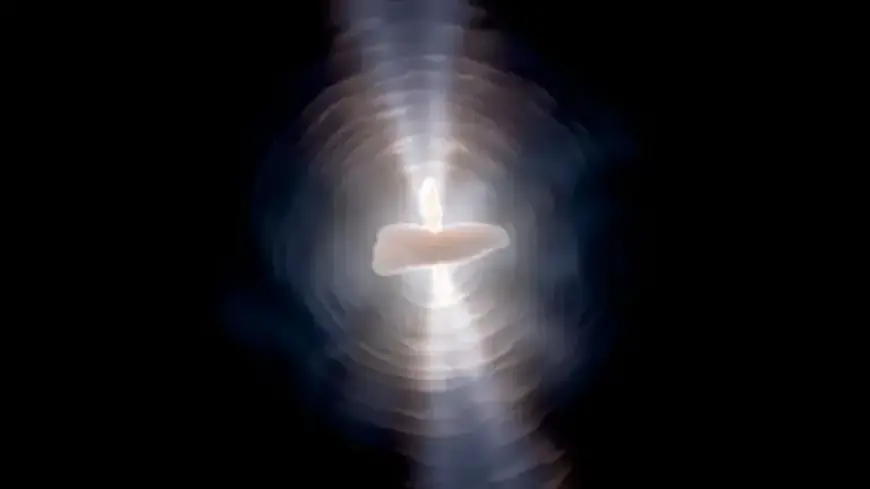

The Egg Nebula is a captivating astronomical object that showcases a unique and intricate structure. Observations made by the Hubble Space Telescope reveal its fascinating three-dimensional architecture. This celestial body is the remnant of a dying star, having expelled multiple shells of gas and dust over the past 5,000 years.
Overview of the Egg Nebula’s Formation
Since its formation, the Egg Nebula has undergone significant changes. Within the last 400 years, it has developed bipolar lobes, expanding outward in a spectacular display. This activity is largely obscured by a dense disk of dust surrounding the star, which plays a crucial role in the nebula’s visual characteristics.
Key Components of the Egg Nebula
- Dying Star: The star at the center is in its final stages of life.
- Gas and Dust Shells: Ejected shells formed over 5,000 years.
- Bipolar Lobes: Expanded within the last 400 years.
- Dense Dust Disk: Hides central star activity, giving a unique appearance.
- Twin Searchlight Effect: Light escapes through poles, resembling two beams of light.
The Role of the Hubble Space Telescope
The visualization provided by the Hubble Space Telescope offers astronomers valuable insights into the Egg Nebula’s structure and dynamics. By analyzing this stunning imagery, researchers can better understand the life cycle of stars and the processes that lead to the formation of nebulae.
In summary, the Egg Nebula is a prime example of stellar evolution. Its complex architecture highlights the fascinating processes of gas and dust ejection from dying stars, adorned with the stunning visuals captured by space telescopes like Hubble.