Quantum Sensors Across Cities Constrain Axion Dark Matter
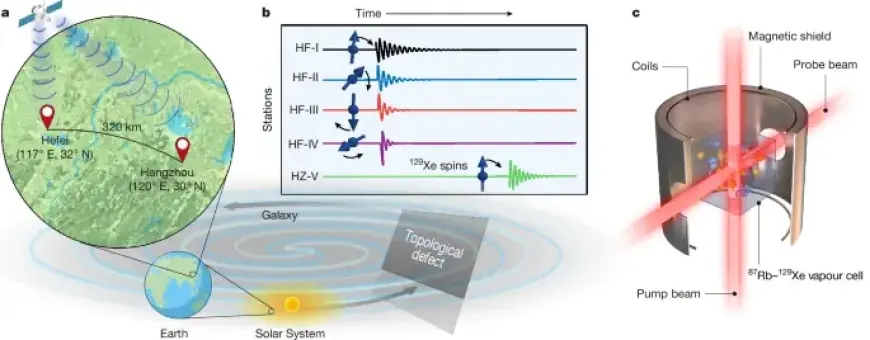
Recent advances in physics have invigorated the search for axion dark matter, a hypothetical particle that may help explain the mysteries of the universe. Researchers are employing quantum sensors across various urban locations to detect these elusive particles.
Quantum Sensors: A New Approach to Dark Matter Detection
Quantum sensors are state-of-the-art devices capable of measuring minute changes in physical systems. These sensors are pivotal in exploring the characteristics and properties of axion dark matter. As scientists work to understand the role of dark matter in the cosmos, they are relying on innovative detection methods.
Key Studies and Findings
- Search for Axion-like Particles: Research teams, including those involved with the Global Network of Optical Magnetometers for Exotic physics searches, are actively probing dark matter using quantum sensors.
- Collaboration Across Cities: The quantum sensors are strategically placed in urban environments, allowing for simultaneous measurements that enhance data collection.
- Significance of Quantum Techniques: Techniques such as atomic clock experiments are being used to enhance the detection sensitivity, as previously noted by researchers like Derevianko and Pospelov.
The collective data from these sensor networks is expected to shed light on axion dark matter’s properties, helping to constrain their characteristics and mass limits.
The Role of Axions in the Universe
Axions are theoretical particles proposed as solutions to fundamental problems in physics, including strong CP violation. They are predicted to have properties that make them excellent candidates for dark matter.
- Theories suggest that axions may form a significant portion of the universe’s missing mass.
- Current experiments aim to discover axions through their interactions with light and other particles.
Recent Research Initiatives
Recent papers highlight various methodologies for detecting axion-like particles. A study published in 2021 emphasized the capabilities of quantum sensors to identify potential signatures of dark matter. Similar initiatives continue to emerge, focusing on harnessing quantum technologies to advance research in particle physics.
As the scientific community pushes the boundaries of research, the combination of quantum sensors and innovative detection strategies marks a promising frontier in the quest to understand axion dark matter. With substantial coordination and collaboration across cities, researchers are optimistic about uncovering essential truths about the universe’s composition.
Conclusion
The exploration of quantum sensors in detecting axion dark matter represents a significant milestone in modern physics. As research continues and technologies evolve, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries remains bright.