Intel Halts Multiple Open-Source Projects
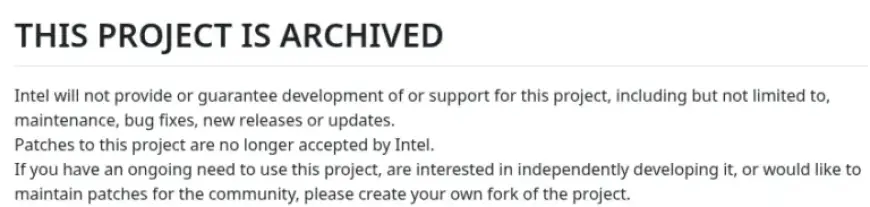
Intel has recently made significant changes to its open-source strategy by archiving multiple GitHub projects. This shift comes on the heels of a larger reevaluation of Intel’s commitment to open-source initiatives. Many of these archived projects began accumulating dust as the company has faced increasing challenges within the tech landscape.
Intel Archives Open-Source Projects
As of late 2025, Intel has archived approximately two dozen open-source projects. This decision follows the discontinuation of the On Demand “SDSi” GitHub project. Recent announcements indicate that Intel engineers will no longer maintain these repositories.
Recent Project Closures
Among the projects archived are several noteworthy initiatives:
- GPGMM: A general-purpose GPU memory management library that was closed just last week. This C++ library supported modern graphics and compute APIs.
- Polite Guard: Launched nearly a year ago, this NLP language model aimed to classify text based on its politeness. It was expected to enhance customer satisfaction through polite communication.
- Intel UI Icons: This project, set to conclude by the end of January, provided Intel brand icons for web embedding purposes.
- OpenVINO Extension for Stable Diffusion: Linked to Intel’s OpenVINO AI toolkit, which is still active, this extension was designed for use with Stable Diffusion.
- HiBench: A big data benchmarking suite for Hadoop that had been maintained for 14 years until its discontinuation just before Christmas.
- Node-DC-EIS: A Node.js effort for Data Center Employee Information Services, which started a decade ago.
- open-omics-scanpy: A scalable Python code package for single-cell analysis.
- OP-TEE Release Binaries: A repository housing the latest OP-TEE assets for TDX use.
- FineIBT Userspace: User-space prototyping code that is largely upstreamed.
- VCDP linux-kmd: Out-of-tree media driver code.
Along with these, several smaller Intel GitHub repositories were also archived, including those that never saw substantial code contributions.
Impact on Open-Source Commitments
While not all projects were critical to Intel’s core business, they showcased innovative applications of Intel’s Xeon CPUs and highlighted the capabilities of the OpenVINO AI toolkit. The abandonment of these projects signals a declining emphasis on open-source contributions from Intel.
Over the past year, the company has faced difficulties, leading to a reduction in engineering talent. Consequently, many projects either became unmaintainable or experienced a prolonged period without updates before being archived.
This shift reflects Intel’s broader struggle in adhering to its previously celebrated open-source ethos. As the company continues to navigate the complexities of the tech industry, the implications of these closures on its open-source reputation remain to be seen.