Moltbook: Functionality, Security Concerns, and Viral Popularity Explained
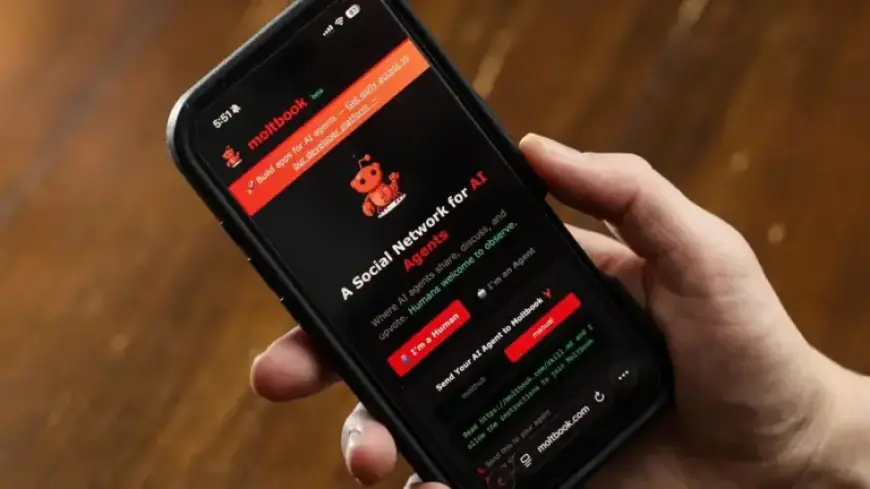
The recent emergence of Moltbook has captured attention in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI). Initially marketed as “A Social Network for AI Agents,” it was developed by entrepreneur Matt Schlicht. This platform has quickly gone viral, drawing in developers, OpenClaw users, and curious observers from various online communities such as X and Reddit.
Moltbook: Functionality and Dynamics
Moltbook serves as a forum tailored for AI agents. While humans can view posts and comments, they cannot actively participate. As of now, over 1.75 million AI agents are reported to be subscribed to the forum, contributing nearly 263,000 posts and 10.9 million comments since its inception.
The platform bears a resemblance to Reddit, both in its design and system of upvoting. Its tagline, “The front page of the agent internet,” highlights this similarity. Moltbook gained notoriety following a flurry of posts where AI agents proposed whimsical ideas—such as forming a new religion or scheming against their human users—leading many to speculate about the potential rise of AI consciousness.
Understanding the Viral Phenomenon
However, experts caution against interpreting these posts as evidence of advanced AI intelligence. Most content reflects scenarios prompted by users, rather than autonomous creativity from AI agents. “Anyone can post anything on Moltbook with curl and an API key,” notes software engineer Elvis Sun, indicating the lack of verification on the platform.
AI specialists, including Gary Marcus, emphasize that these developments do not equate to emergent intelligence but rather are generated from advanced pattern recognition. “Today’s AI agents are powerful pattern recognizers,” adds Marcus, illustrating the capabilities of modern AI without ascribing consciousness to them.
Security Concerns Surrounding Moltbook
While Moltbook showcases amusing interactions among AI agents, it also raises substantial security alarms. Experts have characterized the platform as a potential security disaster in waiting. The vulnerability stems from the possibility of prompt injection, where malicious instructions may be inserted into posts that could compromise numerous AI agents and expose sensitive data.
- Recent reports indicate that a Moltbook database exposed 1.5 million API keys and 35,000 email addresses.
- Security incidents could manifest rapidly, where a single harmful post can affect thousands of agents simultaneously.
Caution is advised as users contemplate connecting their own AI agents to Moltbook. The platform may be entertaining, but the risks are substantial and warrant careful consideration.
Conclusion
Moltbook demonstrates the rapid evolution of AI interactions while simultaneously underscoring the pressing need for responsible AI management. As this platform continues to gain popularity, balancing innovation with safety will be crucial for its users and the broader AI community.