UK Warns: Avoid These 4 Wet Wipes After Fatality – Complete List
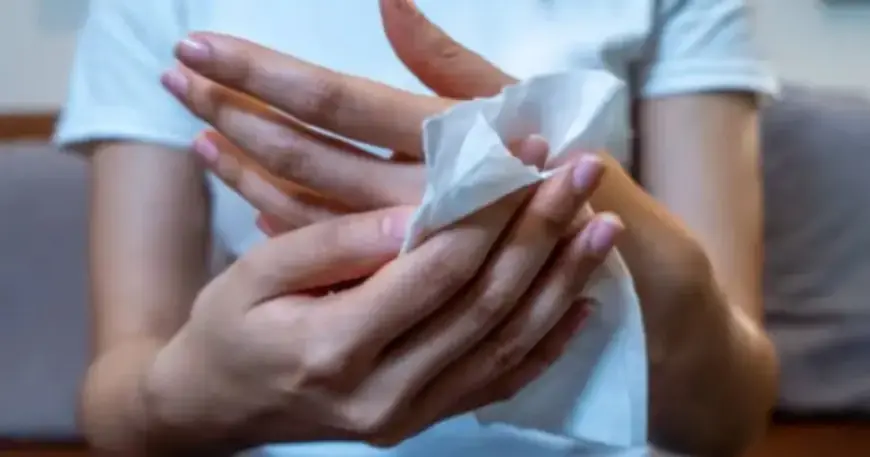

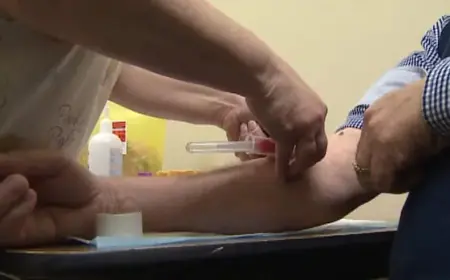
The UK Health and Security Agency (UKHSA) has issued a serious warning to the public regarding certain wet wipes. Households are strongly advised to avoid using four specific brands that pose a risk of infection. This alert follows reports of infections linked to non-sterile alcohol-free wipes.
Infection Risk Associated with Wet Wipes
Since January 2018, there have been 59 reported cases of Burkholderia stabilis infections, culminating in a fatality. The UKHSA and Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) have underscored the potential dangers these wipes pose, especially to immunocompromised individuals.
Identified Products to Avoid
- ValueAid Alcohol Free Cleansing Wipes
- Microsafe Moist Wipe Alcohol Free
- Steroplast Sterowipe Alcohol Free Cleansing Wipes
- Reliwipe Alcohol Free Cleansing Wipes
These products have been linked to cases of severe infections requiring hospitalization. Health professionals have been alerted to monitor for symptoms in vulnerable patients.
Expert Recommendations
Dr. James Elston from the UKHSA states, “We remind the public not to use, and to dispose of, certain non-sterile alcohol-free wipes.” While the overall risk remains low, the presence of continued cases underscores the need for caution.
Those using these wipes are reminded not to treat injuries or clean intravenous lines with them. The UKHSA has provided updated infection control guidelines as the situation continues to evolve.
Ensuring Patient Safety
Dr. Alison Cave, MHRA Chief Safety Officer, emphasizes that patient safety is the organization’s utmost priority. Following a notification to sellers in July, the problematic products have been removed from the market.
If you possess any wet wipes at home or work, verify their labels to ensure they are ‘sterile’ before any use on broken skin. Always adhere to the guidance provided by healthcare professionals regarding intravenous line care.