How I Improved Security by Correctly Using Password Managers
Password managers offer essential security for storing your passwords. However, relying solely on them can introduce risks. Understanding how to properly use a password manager is crucial for enhancing your online security.
Understanding Password Managers and Their Risks
While password managers like Bitwarden, 1Password, and LastPass provide convenience, they can also centralize your risk. If one password manager is compromised, it could expose all the data it holds.
The primary safeguard against unauthorized access is the master password. The belief that your data is automatically protected by the password manager is misleading. In reality, if an attacker manages to access your encrypted vault, they can attempt to crack your master password offline.
Creating a Strong Master Password
- Your master password is the key to your vault.
- A high-entropy passphrase, composed of random words, is easier to remember.
- A complex string is hard for humans to remember but can be easier for computers to guess.
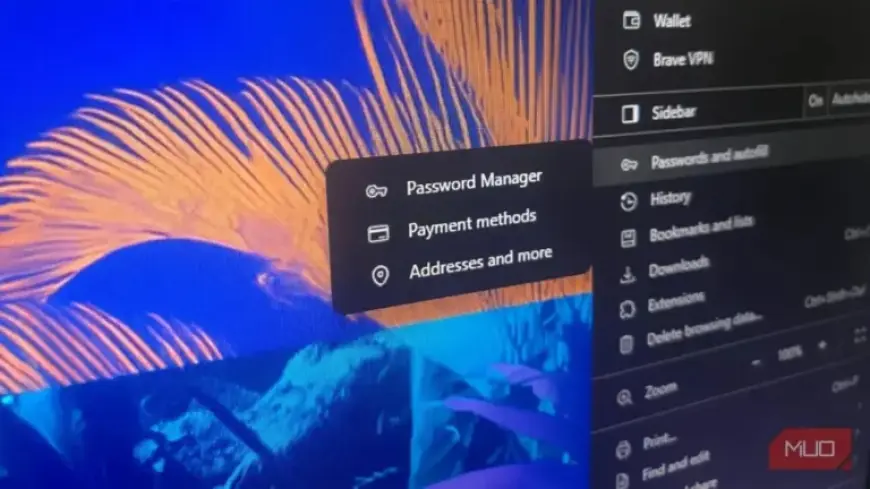
The Autofill Feature: A Potential Security Hole
The autofill feature can be a convenience but also poses security threats. Phishing attackers can exploit this by embedding hidden fields in fake login pages. If your password manager autofills credentials, your information could be captured without your knowledge.
To mitigate this risk, consider disabling autofill entirely. Instead, enter your passwords manually or using keyboard shortcuts for added control.
Separation of Password Management and Two-Factor Authentication
Using the same password manager for all tasks, including two-factor authentication (2FA), diminishes security. If an attacker gains access to your vault, they would also have access to your 2FA codes, undermining the second layer of protection.
To improve security, use a dedicated app for 2FA. For example, moving 2FA codes to an open-source application, like Aegis, or using hardware security solutions such as a YubiKey can enhance your protection.
Finding a Balance Between Convenience and Security
Adopting additional security measures may require extra time. However, investing those extra minutes can significantly boost your security. Reserve the convenience of password managers for less critical accounts.
A tiered approach to security can help balance convenience and risk management. For vital accounts such as banking and email, separate security measures can be essential.
Regular Audits of Your Password Management System
Setting up a password manager is just the first step. Regular audits are necessary to maintain security. Dedicate time to:
- Change your master password periodically.
- Remove duplicate passwords.
- Disable autofill settings.
- Reassess and relocate critical 2FA codes.
In conclusion, while password managers are valuable tools for enhancing security, proactive management is essential. By improving how you utilize password managers, you can significantly strengthen your online security.