Mandiant Unveils Rainbow Tables for NTLMv1 Admin Password Hacking
Google’s Mandiant has released a critical dataset of rainbow tables targeting the outdated Net-NTLMv1 protocol, emphasizing the security risks associated with legacy authentication systems. This release signals a pressing need for organizations to abandon Net-NTLMv1, which has been known to have vulnerabilities since its cryptographic breakdown in 1999. Despite prolonged warnings about its insecurity, many enterprises continue to use this deprecated protocol, underscoring a significant barrier to effective remediation.
Mandiant’s Rainbow Tables for NTLMv1 Admin Password Hacking
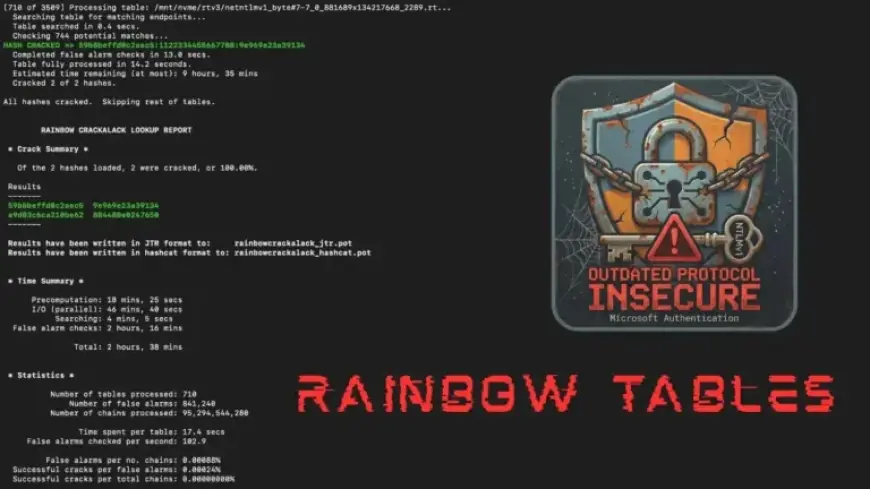
This dataset transforms the landscape of authentication security by dramatically reducing the barriers to credential recovery. Previously, exploiting Net-NTLMv1 required costly hardware or third-party services. Now, security professionals can recover authentication keys in under 12 hours using consumer-grade hardware costing less than $600 USD.
Understanding the Vulnerability
The vulnerability in Net-NTLMv1 arises from its dependence on a known plaintext attack (KPA) mechanism. When attackers obtain a Net-NTLMv1 hash without Extended Session Security (ESS) for the plaintext value “1122334455667788,” they can use cryptographic attacks to recover the key material, corresponding to the password hash of the authenticating Active Directory object.
Attack Methodology
Attackers often initiate their efforts with tools like PetitPotam or DFSCoerce, which coerce authentication from high-privilege targets, such as domain controllers. This leads to capturing Net-NTLMv1 hashes, which are then processed into DES components. Using Mandiant’s rainbow tables alongside tools like RainbowCrack, attackers can recover DES keys to reconstruct the full NT hash, thereby compromising credentials.
- Preprocessing of Net-NTLMv1 hashes into DES components.
- Utilizing tools like RainbowCrack for key recovery.
- Common escalation paths include recovering domain controller machine account hashes.
Availability and Community Response
The dataset is accessible through the Google Cloud Research Dataset portal and can be verified using SHA512 checksums. The security community has started developing implementations optimized for both CPU and GPU processing.
Mitigation Strategies
To counteract these vulnerabilities, organizations are advised to disable Net-NTLMv1 entirely. Configuring Windows systems to “Send NTLMv2 response only” through Local Security Settings or Group Policy is essential. However, organizations should remain vigilant since attackers with administrative access can downgrade settings after a compromise.
Conclusion
The release of Mandiant’s rainbow tables signals a pivotal shift in discussions around the security of Net-NTLMv1. What was once considered an academic issue has unfolded into a practical attack vector that necessitates immediate organizational focus and robust remediation strategies. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are crucial to mitigate these emerging threats.
Stay informed with the latest cybersecurity updates by following us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X. Contact us to feature your stories on Filmogaz.com.