Ligand Activation Paths Define GPCR Cell Signaling
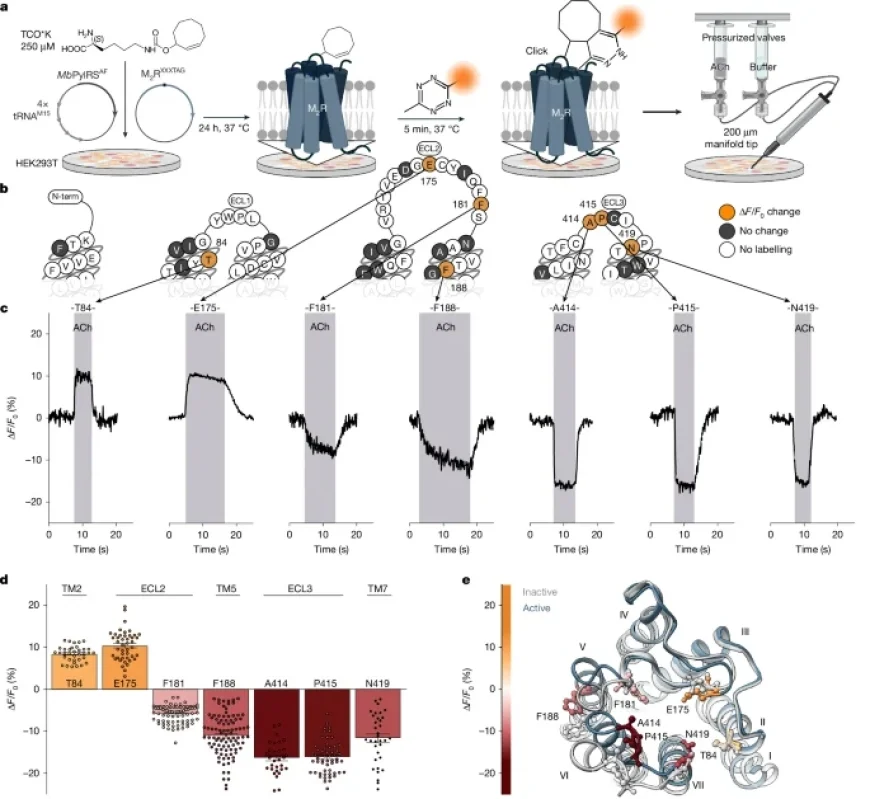
Recent advancements in G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) research have highlighted various ligand activation paths that influence cell signaling processes. This article delves into the methods used to explore the M2 muscarinic receptor (M2R) signaling pathways.
Biosensor Construction
All cloning procedures for generating M2R biosensors utilized Gibson Assembly, using the NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix. Primers for gene amplification were synthesized by BioTeZ, and constructs were verified through Sanger sequencing from LGC Genomics.
- SP-M2R-WT: The wild-type human M2R was cloned into a pcDNA3.0 vector, with a cleavable signal peptide added at the N-terminus.
- SP-M2R-WT-eGFP: Enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) was appended at the C-terminus of SP-M2R-WT.
- SP-HA-M2R-WT: An HA-tag was introduced at the N-terminus for ELISA assays.
Site-Directed Mutagenesis
Mutations were introduced to the receptors by inserting stop codons at specific positions using the AAscan primer design tool. This process involved utilizing templates derived from SP-M2R-WT constructs. The resulting receptor mutants were designated as SP-M2RXXXTAG, SP-HA-SP-M2RXXXTAG, or SP-M2RXXXTAG-eGFP.
Cell Culture Techniques
HEK293T cells were cultured in T75 flasks under controlled conditions. The media was enriched with fetal bovine serum, penicillin, streptomycin, and L-glutamine. Regular passaging occurred when cells reached 80-90% confluency to maintain optimal growth.
- Primary cells: HEK293T and HEK-AD cells used for transfection and assay applications.
- Assay material: Glass-bottomed slides or coverslips coated with poly-D-lysine for enhanced cell attachment.
Transfection and ncAA Incorporation
A two-plasmid system was implemented to facilitate the introduction of non-canonical amino acids (ncAAs) into the receptor proteins. The orthogonal AARS-tRNA pairing enabled the specific incorporation of the ncAAs, enhancing the bioorthogonal labeling capabilities of M2R biosensors.
Live-Cell Imaging
Single-cell fluorescence microscopy enabled real-time observation of receptor activation. Cells were subjected to ligand applications while recording fluorescence intensity over time, revealing dynamic signaling events.
Functional Assays and Labeling
The TRUPATH G-protein activation assay determined the activation profiles of various M2R biosensors by assessing their interaction with different G-protein subunits. Results were documented through quantitative measurements and fluorescence microscopy.
- Cell-surface expression: An ELISA approach confirmed the surface localization of biosensors.
- Labeling efficiency: Bioorthogonal labeling was achieved via click chemistry, which attached the fluorescent dyes to the receptors for imaging purposes.
Statistical Analysis and Data Visualization
Comprehensive statistical methods were employed to validate the experimental results. Metrics included t-tests, ANOVA, and regression analyses to interpret the various relationships between receptor activation and ligand concentration.
Conclusion
The study of ligand activation paths at the M2R highlights its critical role in GPCR cell signaling. The methodologies outlined provide a framework for future research in receptor dynamics and pharmacology, furthering our understanding of cellular communication mechanisms.







































