Potomac River Faces Sewage Spill: Risks Increase with Melting Ice
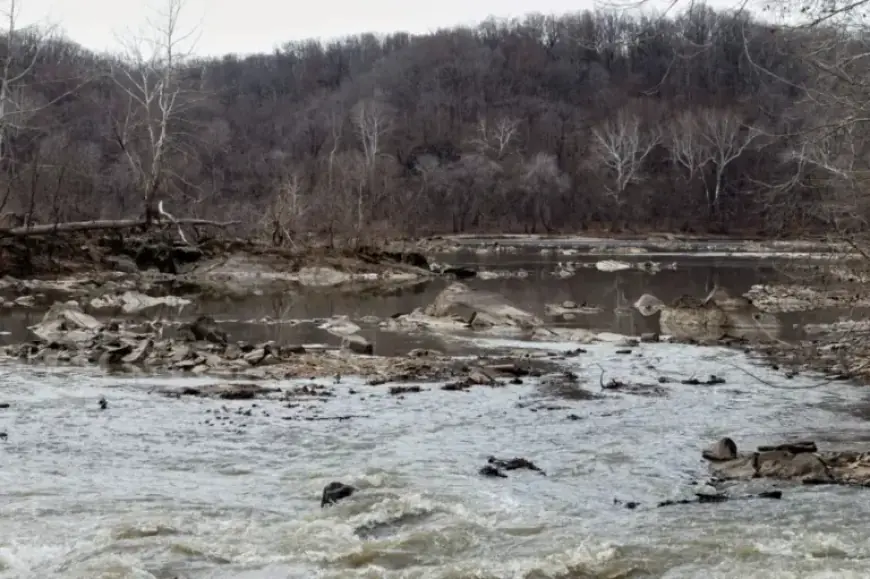

The Potomac River is currently facing serious environmental challenges following a significant sewage spill. In mid-January, a 72-inch sewer pipe, known as the Potomac Interceptor, ruptured, releasing millions of gallons of untreated wastewater into the river. As the situation evolves, concerns regarding the health risks and environmental impacts are escalating, particularly as warmer weather approaches.
Sewage Spill Details and Health Risks
On January 17, D.C. Water reported the failure of the sewer pipe. Since January 21, researchers from the University of Maryland have monitored the river’s water quality weekly. The findings are alarming. Reports indicate E. coli levels exceeding recreational water safety standards by 4,000 times.
- Staphylococcus aureus, including the antibiotic-resistant strain MRSA, has also been detected in the water.
- These bacteria pose significant health risks to individuals who come into contact with the contaminated water or affected land.
Experts Express Concerns
Rachel Rosenberg Goldstein, a professor at the University of Maryland’s Department of Global, Environmental and Occupational Health, emphasized the importance of monitoring water quality. She noted that bacteria thrive in wastewater environments and could proliferate as temperatures rise.
Dean Naujoks, from the Potomac Riverkeeper nonprofit, criticized D.C. Water for underreporting the severity of the spill. He claimed that initial E. coli levels were underestimated, being 100 times higher than reported. Naujoks urges local and federal authorities to take more decisive action in informing the public about the risks.
Government Response
In response to the situation, D.C.’s Department of Energy and Environment issued a strong advisory. Residents and pets are advised against any contact with the Potomac River or participating in recreational activities, including fishing.
Ongoing Monitoring Efforts
The department is conducting ongoing tests at multiple sites along the Potomac and Anacostia rivers to assess contamination levels. D.C. Water is also involved in testing additional locations. Results will be shared with the public weekly.
As the ice covering the river thaws, the risk of bacterial growth will likely increase. Maintaining public confidence in the safety of the Potomac River will require thorough, transparent, and ongoing monitoring efforts.
For more updates on environmental safety and news, stay tuned to Filmogaz.com.