Understanding Your Legal Rights During ICE Encounters: Expert Insights
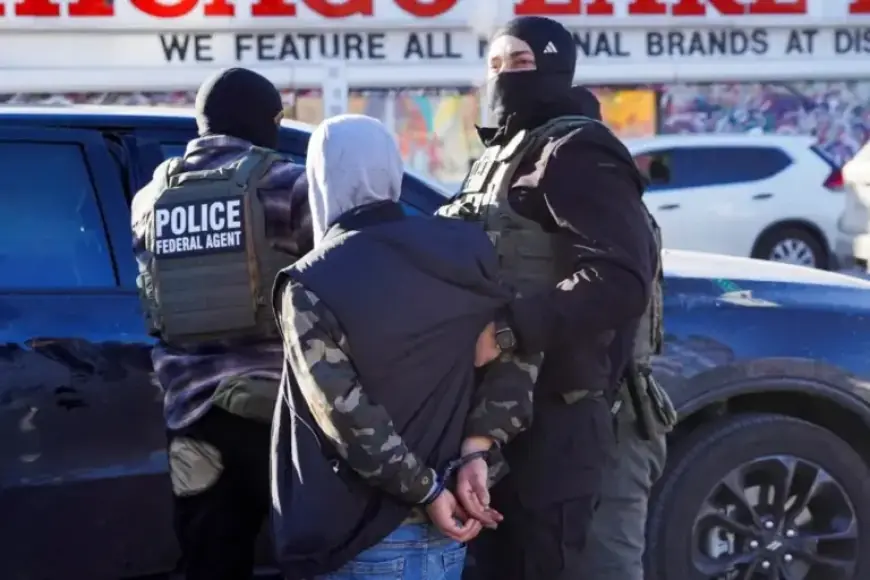

Recent events in Minneapolis have drawn attention to the actions of Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agents. Reports indicate that ICE has deployed around 3,000 officers in the city to conduct stops, questioning, and detentions of residents. Among the alarming incidents reported, a U.S. citizen of Hmong descent was escorted from his home by agents while wearing only his underwear, and a father was temporarily detained after being questioned about his citizenship based on his accent.
These confrontations have raised significant questions about the legal rights of individuals during ICE encounters. Are there clear boundaries regarding ICE’s authority in public versus private settings? Legal experts have begun to weigh in on these matters, particularly regarding constitutional protections against unreasonable searches and seizures.
Understanding Your Legal Rights During ICE Encounters
Constitutional Protections
The Fourth Amendment safeguards all individuals from unreasonable searches and seizures. This protection extends to everyone, including immigrants suspected of being in the U.S. illegally. Alexandra Lopez, a managing partner at a Chicago law firm specializing in immigration, emphasizes that all law enforcement officers, including those from ICE, must adhere to constitutional standards.
Standards of Detention
ICE agents require a “reasonable suspicion” to conduct brief detentions. This means they must have specific, articulable facts suggesting that a crime has occurred or is about to occur. Michele Goodwin, a law professor at Georgetown University, notes that reasonable suspicion must exceed mere guesses.
To arrest someone, ICE must meet a higher threshold known as “probable cause.” This necessitates sufficient evidence indicating that a crime has been committed. The recent legal landscape has also seen cases where immigration enforcement tactics face significant scrutiny.
The Impact of Recent Supreme Court Rulings
Supreme Court Justice Brett Kavanaugh’s recent opinion has allowed increased discretion for ICE in using race as a factor in determining reasonable suspicion. This change has sparked concerns regarding possible ethnic profiling during these encounters. Critics argue that this could lead to more aggressive enforcement actions, although the overall legal ramifications of this opinion remain ambiguous.
Rights in Private Spaces vs. Public Areas
Legally, ICE requires a judicial warrant to enter a private residence unless consent is given. The Supreme Court generally mandates that without a warrant, agents cannot enter homes. However, exceptions exist, such as during urgent circumstances. Lopez notes that it is typically easier for ICE to detain individuals in public settings due to the heightened requirements for private home entries.
Administrative warrants issued by ICE itself are another point of contention. These warrants do not undergo judicial review, which raises questions about their constitutionality. A leaked memo indicated that ICE officials were instructed on entering homes using only administrative warrants, despite opposing guidelines.
What to Do If Your Rights Are Violated
If individuals believe their rights have been infringed during an ICE encounter, options for legal recourse are limited. Federal law often protects officials from civil lawsuits, complicating the path to justice. However, it may be possible to sue under the Federal Tort Claims Act, although this too presents significant challenges.
Legal experts, including David Rudovsky from the University of Pennsylvania, highlight that while the avenue exists, it is not straightforward, and many may struggle to afford legal representation.
As debates on immigration policy continue, understanding your legal rights during ICE encounters remains crucial. Knowledge of these protections can empower individuals facing potential confrontations with immigration enforcement.