Rising Measles Cases in England: Potential Spread Locations Identified
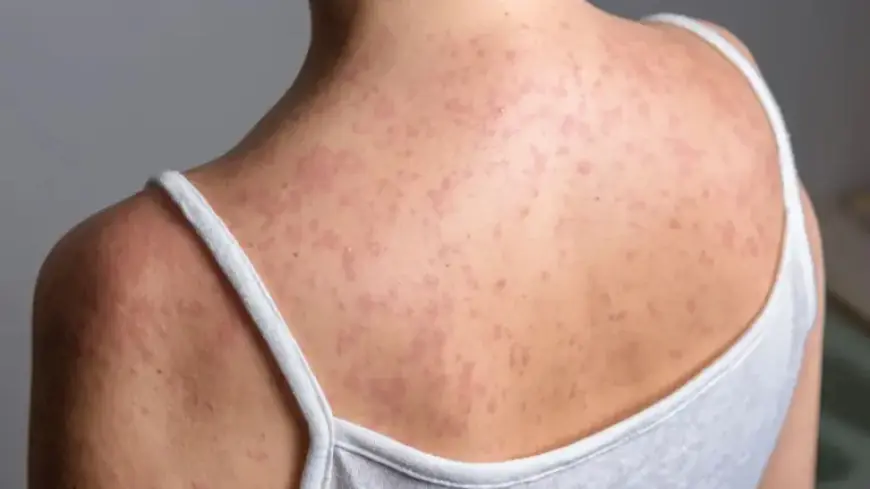
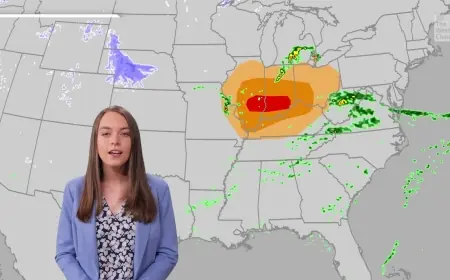
Cases of measles are on the rise in England, predominantly affecting unvaccinated children. As of Monday, the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) reported 130 confirmed cases this year. The outbreak has been particularly concentrated in Enfield, a borough in north London, which has recorded 50 cases.
Potential Spread Locations Identified
Recent data indicates that a significant portion of the outbreak took place between February 12 and 16, with 34 cases confirmed during this brief period. Nearby councils, including Southend City Council, are concerned that the rising prevalence in Enfield could lead to infections spreading to areas such as Essex, Southend, and Thurrock.
Health Risks and Recommendations
Experts warn that the true number of cases might be higher due to delays in laboratory confirmations. Dr. Vanessa Saliba, a consultant epidemiologist at UKHSA, emphasizes that the outbreak predominantly affects unvaccinated children under the age of ten who attend schools and nurseries.
- Measles can lead to serious health complications, including pneumonia and brain inflammation.
- Complications can result in long-term disability or even death in rare cases.
- The disease is highly contagious among unvaccinated individuals.
Dr. Saliba urges parents to ensure their children are vaccinated with the MMRV vaccine, which requires two doses for effective protection. This vaccine is critical in safeguarding not only the vaccinated children but also those who cannot be vaccinated, such as the very young or those with weakened immune systems.
Public Health Implications
The concerning measles outbreak in England has prompted urgent calls for vaccination awareness. Parents are encouraged to consult with their general practitioners to verify vaccination status. It is timely for those who may have missed doses to catch up, as protecting children from measles is vital.
As the World Health Organization has noted, the UK is no longer regarded as having eliminated measles. This resurgence underscores the importance of maintaining high vaccination coverage to prevent future outbreaks.