Home Insurers Hike Rates, Tighten Coverage Amid Rising Weather Threats
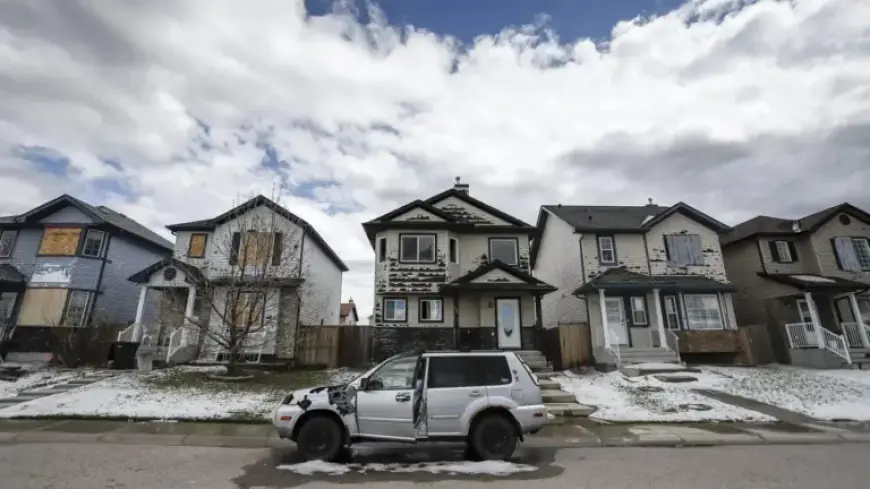

As extreme weather events rise, Canadian home insurers are adjusting their strategies to manage increasing risks. The industry faces significant challenges, compelling insurers to hike premiums and tighten coverage. These changes reflect a growing concern over financial sustainability in an unpredictable climate.
Insurance Premium Increases and Coverage Adjustments
In recent years, home insurance rates in Canada have risen significantly, exceeding inflation levels. Insurers have responded by:
- Increasing premiums substantially.
- Excluding certain risks from their coverage.
- Raising deductibles, some reaching $10,000.
- Reducing their market presence in higher-risk areas.
According to a November report by Morningstar DBRS, early signs of coverage tightening are evident in the Canadian insurance market. This adjustment is part of a broader strategy to mitigate risks associated with severe weather events.
Insurers’ Strategic Moves
Companies like TD Bank are rebalancing their exposure to higher-risk zones. CEO Raymond Chun noted a shift toward regions less vulnerable to extreme weather. Similarly, Definity Financial Corp. is actively reducing its footprint in high-peril areas following its recent $3.3 billion acquisition of Travelers.
Definity’s CEO, Rowan Saunders, expressed that the company is focusing on portfolio management by redirecting new business away from regions with high catastrophe exposure. Such moves are crucial as Canada faces escalating insured losses, exemplified by a record $9.4 billion in 2024.
Rising Catastrophic Events and Their Impact
Between 2020 and 2024, the number of catastrophic weather events in Canada averaged 15 annually, a stark increase from two per year in the 1980s. This spike in extreme weather has led to considerable personal property losses, placing immense pressure on the home insurance sector. Economist Likeleli Seitlheko noted the substantial strain these losses place on insurers.
Insurers have reacted to these soaring costs by:
- Implementing higher deductibles on specific risks.
- Reducing or eliminating coverage for perilous events, particularly flooding.
The Challenge of Flood Insurance in Canada
Flood insurance availability remains inconsistent. Approximately 1.5 million households lack access to flood insurance, translating to about 10% of Canadian homes. For those who can obtain coverage, annual premiums may increase by as much as $15,000. However, experts dispute industry claims of widespread availability, suggesting that effective access may be closer to 50% due to risk profiling and market redlining.
Public Safety Canada cites Quebec as having the most flood-prone properties, followed by Ontario and British Columbia. Any improvements in flood mapping are crucial for addressing these risks as insurers continue to adapt.
Stability Amidst Increasing Costs
Despite the rising costs and challenges faced, the home insurance sector in Canada remains stable. Nadja Dreff from Morningstar DBRS emphasized that the 2024 losses served as a stress test, highlighting the industry’s preparedness. However, the resultant need for premium increases creates difficulties for consumers.
From 2021 to 2025, home insurance costs surged by 31%, significantly surpassing the overall inflation rate of 15%. Notably, regions affected by numerous claims saw even greater spikes, with British Columbia experiencing an average 68% increase, while Alberta saw a 58% rise.
The Path Forward: Building Resilience
In light of these developments, industry leaders like Liam McGuinty of the Insurance Bureau of Canada advocate for investments in climate resilience. As housing projects ramp up, McGuinty stresses the importance of responsible development that avoids flood zones and prepares for other extreme weather risks.
Ultimately, increasing costs driven by climate change will impact policyholders directly. As the sector evolves, all stakeholders must prioritize building a more resilient future.