New Map Reveals Dark Matter Distribution Across the Universe
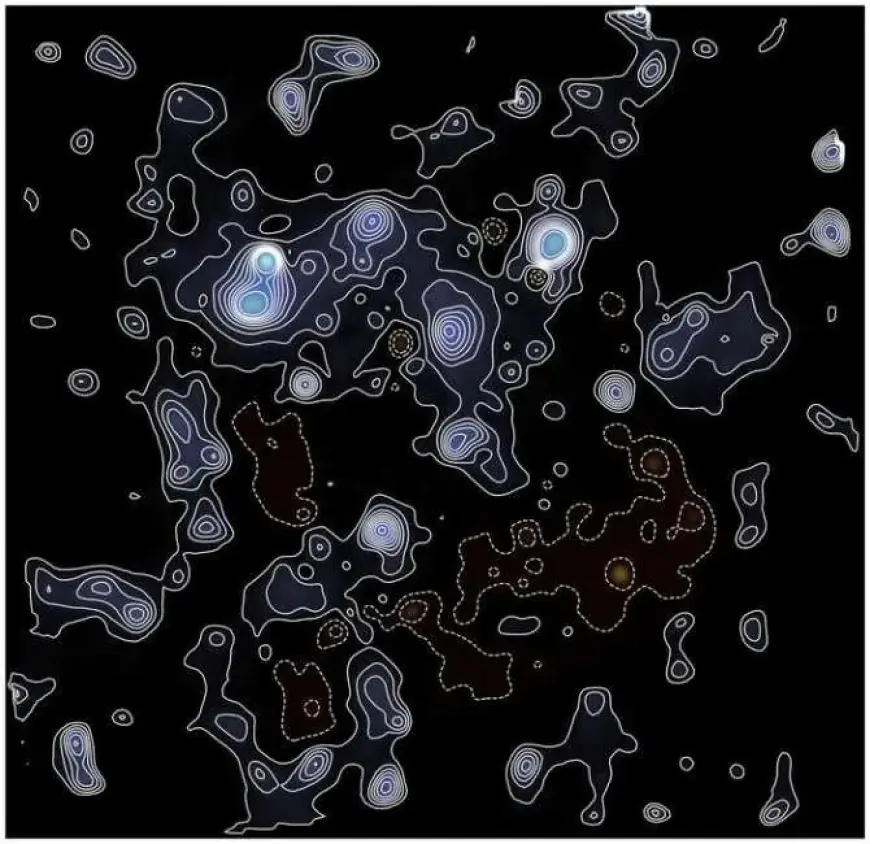
Recent advancements from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have led to the creation of a groundbreaking map detailing dark matter distribution throughout the universe. This intricate map sheds light on the vital role dark matter has played in shaping the universe’s structure.
Key Figures Behind the Research
The study is headed by Diana Scognamiglio from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Gavin Leroy from Durham University in the UK. Both researchers contributed their expertise to interpret the complex data collected from the JWST.
The Role of Dark Matter
Dark matter is an enigmatic form of matter that does not emit electromagnetic radiation but has a significant gravitational influence. It is more prevalent in the universe compared to regular matter, which includes everything we can touch or observe. Importantly, dark matter is neither black holes nor any known celestial body.
Methodology of the Study
- Galaxies were examined to map out dark matter’s distribution.
- Researchers detected dark matter through its gravitational effects, which curve space and light.
- The resulting map reveals regions with varying densities of dark matter.
This new mapping confirms previous research findings and enhances our understanding of the relationship between dark matter and ordinary matter. Initially, both dark and ordinary matter were dispersed throughout the universe.
The Formation of Structure in the Universe
Dark matter is believed to have clumped together first, subsequently attracting normal matter. This process led to the formation of clumps where stars and galaxies began to emerge. This mechanism has significantly influenced the large-scale distribution of galaxies observable in the present universe.
Significance of Dark Matter
A striking revelation from the study is that dark matter is essential for the formation of galaxies and stars. In turn, it also created the conditions necessary for planets, potentially leading to the rich chemical diversity present in our galaxy.
Richard Massey, a researcher from Durham University, emphasized the omnipresence of dark matter, stating, “Billions of dark matter particles pass through your body every second without causing harm.” He highlighted that the gravitational pull of dark matter is crucial for the cohesion of the Milky Way galaxy, preventing it from disintegrating under its rotation.
Publication and Future Research
The findings of this pivotal study, titled “An ultra-high-resolution map of (dark) matter,” were published in the academic journal Nature Astronomy. The research opens avenues for further exploration into dark matter’s influence on cosmic structures.