Bullock Ties Government Spending to Rate Hike Amid Chalmers Criticism
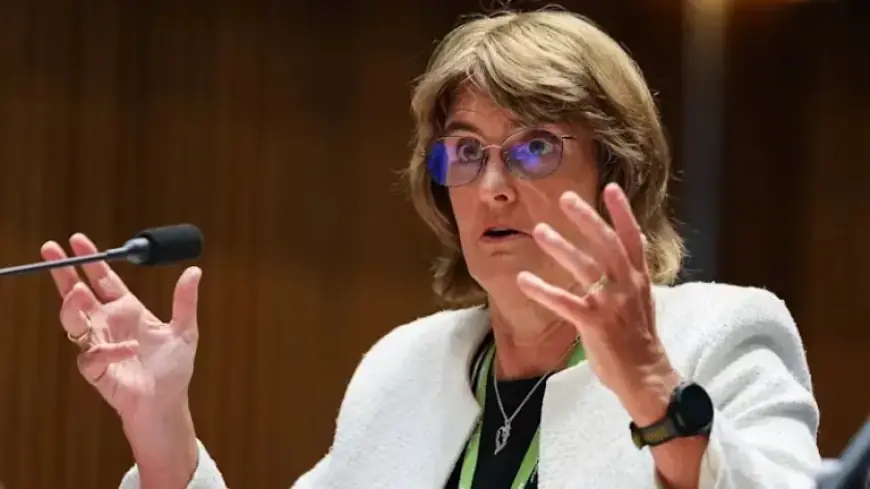

Reserve Bank governor Michele Bullock has linked government spending to the recent decision to increase interest rates. This announcement has drawn criticism from Treasurer Jim Chalmers, who has attempted to separate himself from rising inflation pressures. Bullock’s remarks came during a three-hour session of questioning by Liberal members of the House economics committee.
Bullock Highlights Government Spending’s Impact on Inflation
During the committee hearing, Bullock acknowledged that both private and government spending are driving demand, contributing to inflation. She confirmed that these expenditure patterns are creating aggregate demand stronger than the economy can supply. As a result, inflation is expected to remain above 3 percent for the foreseeable future.
Treasurer Chalmers Faces Opposition Pressure
Chalmers has faced mounting pressure since the Reserve Bank raised the cash rate by a quarter percent. The increase follows a trend in which government spending is anticipated to reach a five-year high of 26.9 percent of the economy by 2025-26.
- Government spending expected to increase by $60 billion this financial year.
- Record spending projected at $786.6 billion.
In response to the rate hike, Chalmers attributed inflation pressures primarily to private demand rather than public spending. He asserted that the Reserve Bank did not mention government actions as a factor in its decision.
Controversy Over Economic Policy
Shadow treasurer Ted O’Brien criticized Chalmers, claiming Bullock’s statements undermined his position. He stressed the importance of accountability regarding inflation and spending.
Conversely, Chalmers defended his stance, indicating that the growth of private-sector demand is significant. He mentioned that the government recognizes public demand as part of overall economic activity, countering claims from the opposition.
Future Implications of Rate Increases
The Reserve Bank’s decisions may lead to further hikes in the near future. Economists anticipate that the cash rate will increase again by another quarter percentage point at the upcoming June meeting.
| Potential Cash Rate Increase | Expected Rate |
|---|---|
| Next Meeting (June) | 4.1% |
While some experts believe the bank may raise rates further, Bullock emphasized that countries like Canada and New Zealand have opted for much higher rates at the expense of job markets. Her commentary highlights the delicate balance between controlling inflation and maintaining economic stability.
As the economy navigates these challenges, the impact on household spending will become increasingly relevant. Research indicates that many borrowers have maintained steady mortgage repayments, which may mitigate some effects of rising interest rates.
This complex situation continues to evolve, underscoring the interconnectedness of government policy, consumer demand, and inflationary pressures.