Controversy Surrounds EU-Mercosur Deal: Why Some Are Unhappy
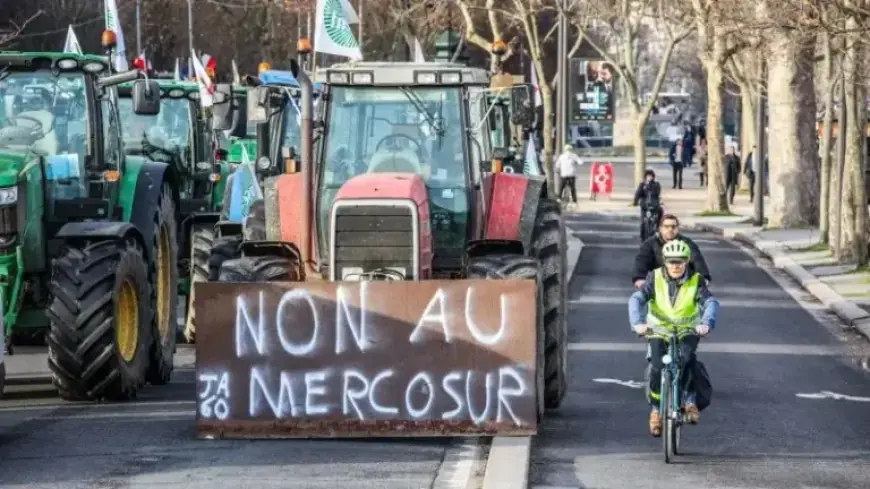

The EU-Mercosur trade agreement aims to remove tariff barriers that currently hinder trade between Europe and South America. Many goods are costly to import or export due to these tariffs. The agreement is expected to eliminate tariffs on approximately 91% of goods traded between the two blocs.
Trade Implications of the EU-Mercosur Deal
The tariff reduction is significant. For instance, the trade-weighted effective tariff rate on EU exports to Argentina is projected to drop from 10.3% in 2024 to around 1%. Current tariffs can reach as high as 35% for car parts and automobiles, and 28% for dairy products.
- Tariffs on car parts will be eliminated linearly over ten years.
- The EU will implement a tariff rate quota for beef over a five-year period.
Overall, the removal of tariffs could save about $4 billion. However, the implementation of these changes will occur gradually, tailored to each specific product.
Legal Framework of the Agreement
The agreement comprises two main legal instruments. The first is the interim Trade Agreement (iTA), which focuses primarily on trade issues. The iTA will become effective once approved by the European Parliament and finalized by the Council through a qualified majority.
The second instrument is the EU-Mercosur Partnership Agreement (EMPA), which has a broader range of topics, including political dialogue, cooperation, investment, and environmental measures. For the EMPA to be fully implemented, all 27 EU member states must ratify it, a process that can extend over several years.
Provisional Application and Ratification Challenges
To avoid delays, the European Commission has recommended provisional application of certain EMPA provisions, specifically those related to political and cooperation measures. Historical examples indicate that the ratification process is often slow. The EU-Canada Agreement (CETA), for example, has been provisionally applied since 2017, yet only 17 of the 27 member states have completed ratification.
While CETA faced delays due to its extensive investment provisions, the EMPA contains fewer such complexities. Nonetheless, ongoing discussions surrounding ambitious sustainability commitments could pose additional challenges to the agreement’s smooth passage.