Unveiling Ghost Lineages: Ancient DNA Remnants Within Us Today
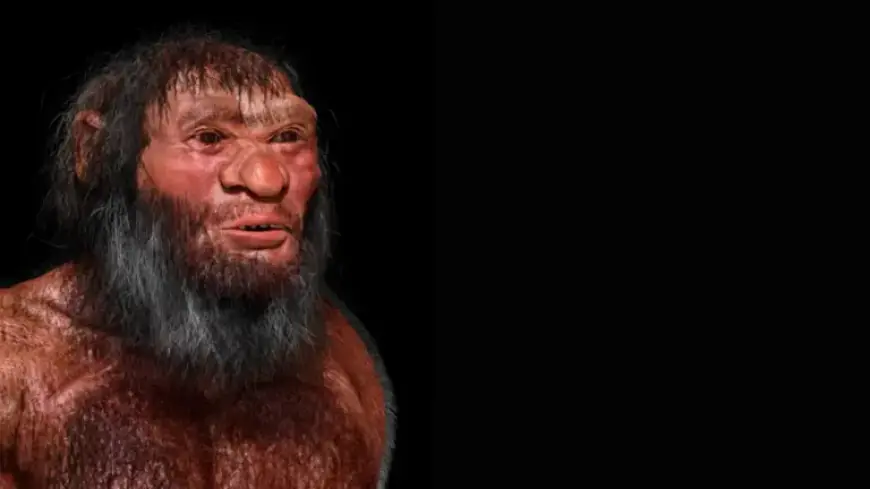

Recent studies on ancient DNA have brought to light the concept of “ghost lineages,” an intriguing aspect of evolutionary genetics. Unlike conventional extinct species, ghost lineages refer to populations that have vanished without leaving direct fossil evidence. Instead, their genetic legacy continues to influence present-day species.
Understanding Ghost Lineages
A ghost lineage is effectively an extinct population that still affects the genetic makeup of existing organisms, including humans. University of Wisconsin-Madison palaeoanthropologist John Hawks recently described these ancient groups as integral to the genetic history of current populations.
Love Dalén, an evolutionary geneticist at Stockholm University, noted that discoveries of ghost lineages in animals often occur unexpectedly. Research initially aimed at understanding the evolution of extinct species, such as mammoths and lemmings, has resulted in significant findings related to genetic heritage.
Discoveries from Ancient DNA
As researchers analyze ancient DNA from specimens like frozen mammoth fossils, they uncover distinct ghost lineages. These findings suggest that genetic diversity was broader during the last ice age compared to today. Dalén emphasized the importance of these findings in understanding historical biodiversity, especially among Arctic species.
- Genetic diversity in Arctic species was considerably higher in the past.
- Ghost lineages inform us about ancient populations that contributed to current genetic structures.
Ghost Lineages in Human Evolution
The identification of ghost lineages in human genealogy is particularly fascinating. Research has transformed our understanding of human evolution from a linear model to a more complex, “bushier” framework. This indicates that various ancient populations contributed to the human genetic pool, challenging the notion of straightforward evolutionary progress.
Over the past two decades, genetic research has revealed these ghost lineages in modern humans and their extinct relatives. The findings indicate that archaic groups, which existed for hundreds of thousands or even millions of years, significantly impacted today’s human genome.
The Complexity of Human Evolution
Michael Petraglia, a paleoanthropologist at Griffith University, pointed out that the ongoing discoveries of ghost lineages illustrate the intricate nature of our evolutionary tree. This “braided stream” model depicts an extensive array of ancient groups influencing modern humans.
- Ghost lineages provide insights into the evolutionary history that the fossil record fails to capture.
- Research into these lineages enhances our understanding of interbreeding events among early hominins.
Insights from Superarchaic Ancestors
The existence of a “superarchaic” lineage, which diverged from our ancestral tree between 2 million and 1.8 million years ago, has also been deduced through genetic analysis. Although no fossils of this lineage have been discovered, its genetic traces have been identified in the genomes of modern populations in West Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
Interbreeding among various groups, including Denisovans, Neanderthals, and modern humans, has complicated the understanding of these ancient lineages. Petraglia noted that genetic evidence suggests significant interactions among these groups, leading to a richer genetic tapestry in contemporary humans.
The Future of Human Evolution Studies
Current research is revising the narrative of human evolution, indicating a far more intricate history than previously thought. Each discovery brings fresh insights into the evolutionary processes that have shaped humanity today.
These ongoing investigations into ghost lineages not only deepen our understanding of biodiversity but also illuminate the complex pathways of human ancestry. As scientists unravel the roles of these ancient populations, they continue to transform our comprehension of what it means to be human.