NASA Satellite Captures Stunning Polar Vortex Image: February 4, 2026 Highlight
The recent winter storm that impacted the United States in late January triggered a significant outbreak of Arctic air. This cold front pushed temperatures dramatically below seasonal averages, affecting areas from the Midwest to the South. The aftermath of the storm left a chilling grip on many regions, with snow and ice creating hazardous conditions.
NASA Satellite Captures Stunning Polar Vortex Image: February 4, 2026
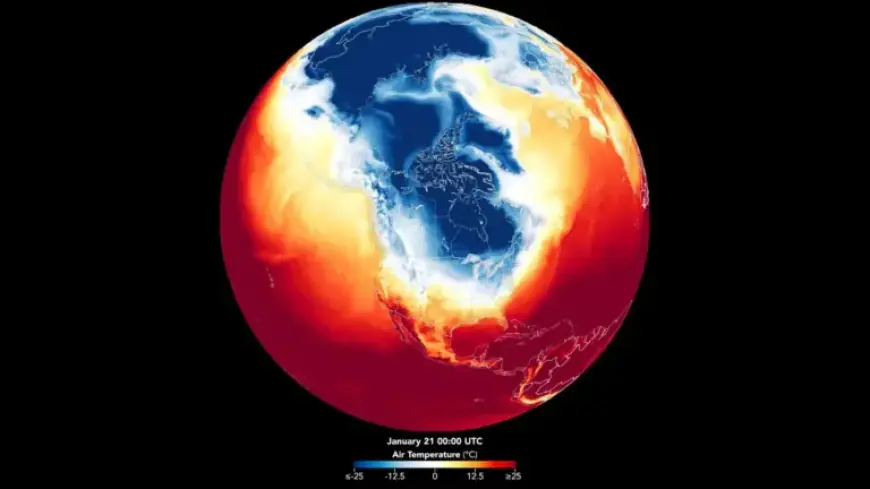
To analyze the broader implications of this winter storm, NASA utilized data from its Earth Observatory combined with temperatures modeled by the Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS). This approach allowed scientists to map out the polar vortex and its effects on temperatures across North America.
Understanding the Polar Vortex
The polar vortex refers to large areas of cold air that can move southward, leading to extreme winter conditions. During this event, near-surface air temperatures were noticeably colder, shown in deep blue on temperature maps. The data revealed unusual patterns as frigid air moved south and east, persisting throughout the week instead of retreating as usually expected.
Weather Patterns and Implications
Meteorologists explained that this pattern was driven by strong high-pressure systems, which forced the jet stream into a deep dip. This configuration enabled cold Arctic air to spill into lower latitudes, impacting millions of people.
- Dates of Polar Vortex: January 21 to January 27
- Affected areas: Midwest, South, Eastern North America
- Key impacts: Power outages, infrastructure damage, health risks
The Importance of Satellite Data
Nasa’s satellite imagery provided valuable insights into the polar vortex’s structure and movement. By creating a time-lapse video of the phenomenon, researchers could visualize how the cold air mass extended over North America. This information is critical for emergency management and recovery strategies.
Extreme winter weather not only disrupts daily life but also poses risks such as hypothermia and frostbite. Prolonged exposure to low temperatures can strain public services and emergency response systems. Enhanced mapping of winter storm patterns can greatly aid decision-makers in prioritizing resources and recovery efforts.
For those interested, further information about Earth-scanning satellites and environmental science can be found at Filmogaz.com.