Parliament Approves New Hate Laws: What Impact Will They Have?
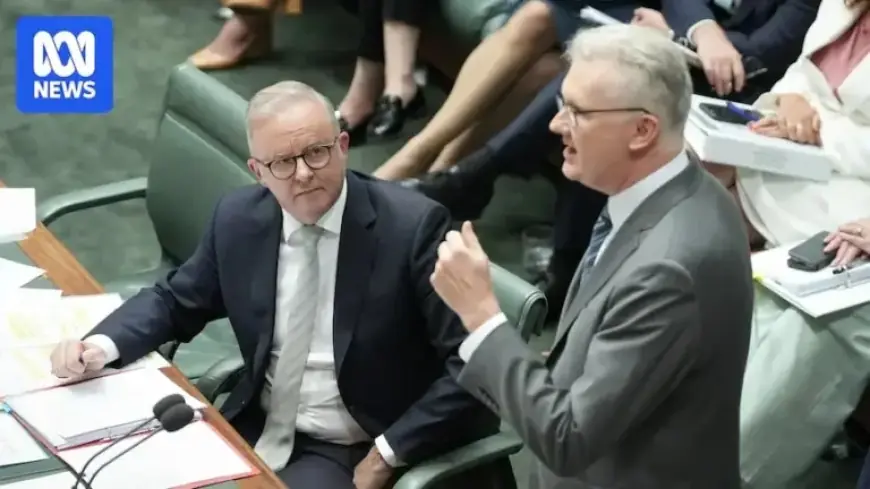

The Australian Parliament has recently approved significant federal legislation aimed at combating hate speech and hate groups, marking a historic change in the country’s legal landscape. This legislation follows the Bondi terror attack, focusing primarily on addressing antisemitism, with Labor leading the charge for its implementation.
Key Features of the New Hate Laws
The newly enacted laws, which received bipartisan support from the Liberal Party, are seen as a robust attempt to tackle hate-driven activities. However, they faced opposition from the Nationals, Greens, and One Nation, who raised concerns about potential infringements on free speech.
- Criminalization of Hate Speech: The legislation makes it an offense to promote or incite racial hatred.
- Definition of Hate Groups: Hate groups are now defined as organizations inciting hatred or violence based on race, national, or ethnic origin.
- Increased Government Powers: Authorities can list hate groups, deport individuals linked to them, and impose harsher penalties for hate crimes.
Background and Legislative Journey
Key recommendations from antisemitism envoy Jillian Segal influenced the bill’s framework, with strong backing from Jewish organizations. However, after the Coalition and Greens expressed concerns about the implications for free speech, Prime Minister Anthony Albanese withdrew a contentious provision from the draft legislation.
Concerns and Criticism
Critics, including members of the Greens, argue that the laws could stifle political discourse and silence critiques of foreign nations engaged in human rights violations. Legal experts have raised alarms about the legislation’s vagueness and its potential to lead to unintended legal challenges.
- Chilling Effect on Speech: Opponents claim the laws could inhibit legitimate discussion and protest.
- Procedural Fairness Issues: There are no requirements for procedural fairness when listing hate groups, raising concerns about justice and accountability.
Impact on Radicalization and Youth
One of the significant aspects of the legislation is its focus on preventing the radicalization of youth. New aggravated offenses targeting adults attempting to radicalize children have been introduced as part of the reforms.
| Age Group | Investigated Since 2020 | Charged with Terrorism-Related Offences |
|---|---|---|
| 12-17 years | 48 | 25 |
According to data from the Australian Federal Police, a significant percentage of youth involved in terrorism-related investigations exhibited religious motivations. Experts believe that while the new laws aim to curb extremist behaviors, they may not significantly alter existing social dynamics associated with radicalization.
Looking Ahead
The implementation of these laws represents a critical step in Australia’s approach to hate speech and radicalization. Nonetheless, ongoing discussions about free speech rights and the balance between security and civil liberties will continue to shape the discourse surrounding these new legal frameworks.