China Unveils Xuntian Space Telescope Capabilities Ahead of 2027 Launch (Video)
China is making significant strides in space exploration with the upcoming launch of the Xuntian Space Telescope. This powerful observatory is set to orbit alongside the Tiangong space station, with a targeted launch date in early 2027. Recent simulations conducted by Chinese scientists have prepared the telescope for its ambitious mission.
Xuntian Space Telescope Overview
The Xuntian Space Telescope, officially known as the Chinese Space Station Telescope (CSST), boasts a primary mirror measuring 6.6 feet (2 meters) across. Although its mirror is slightly smaller than that of the Hubble Space Telescope, Xuntian is designed to surpass Hubble’s capabilities as a sky survey instrument.
Key Features
- Camera Quality: The telescope features a 2.5-billion-pixel camera.
- Field of View: Xuntian has a field of view approximately 300 times larger than Hubble.
- Wavelength Range: It will observe the sky from near-ultraviolet to near-infrared wavelengths.
- High Spatial Resolution: The telescope is expected to deliver detailed imagery of celestial objects.
Preparation and Testing
To ensure optimal performance, a team of researchers created a comprehensive end-to-end simulation. This simulation replicated both the optical and observational conditions the telescope is likely to encounter. The results of these tests were shared in the journal Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics earlier this January.
Scientific Contributions
The Xuntian Space Telescope aims to contribute to multiple fields of study, such as:
- Cosmology
- Galactic research
- The evolution of stars and planets
- Understanding dark matter and dark energy
Launch and Operations
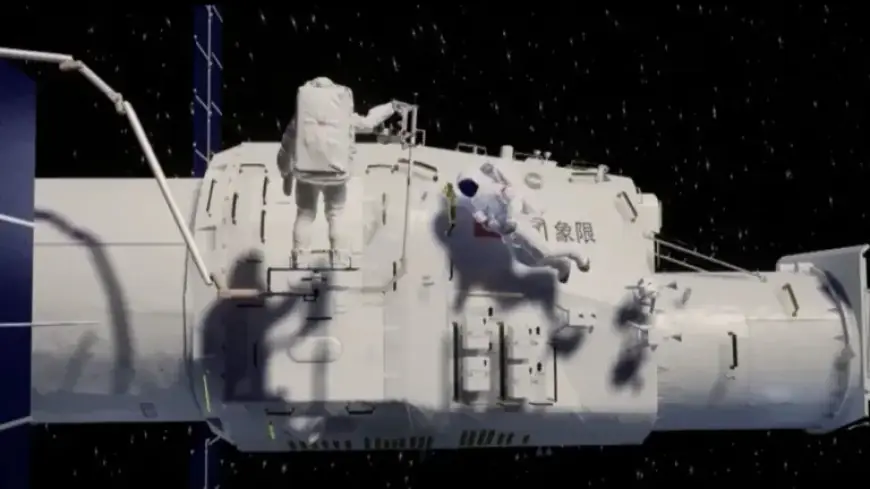
The Xuntian Space Telescope will be launched onboard a Long March 5B rocket. Upon entering low Earth orbit, it will co-orbit with the Tiangong space station. A video released by China Central Television (CCTV) highlights the telescope’s capability to dock with Tiangong.
This docking feature enables astronauts to perform extravehicular activities for maintenance, repairs, or upgrades, similar to the maintenance missions conducted on Hubble by NASA astronauts between 1993 and 2009.
As the launch approaches, the scientific community eagerly anticipates the discoveries that Xuntian will unveil, promising a new era of astronomical research.